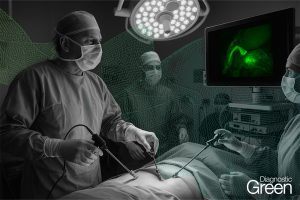
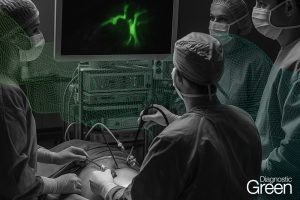
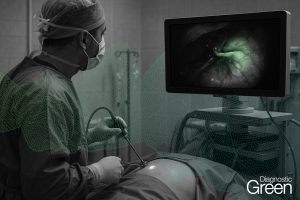
Aim: This study aimed to clarify the clinical effects of the indocyanine green (ICG)-fluorescence imaging (FI) technique for determination of liver transection lines during laparoscopic partial liver resection for liver tumours. This was a retrospective study including 112 patients who underwent laparoscopic partial liver resection for liver tumours. These enrolled patients were divided into an ICG-FI group (n = 55) and a non-ICG-FI group (n = 57) according to the availability of the ICG-FI. The clinicopathological characteristics of patients between two groups were compared before and after propensity score matching.
Results: The ICG-FI and non-ICG-FI groups differed at baseline in terms of ICG retention rate at 15 min. After propensity score matching, two comparable groups of 32 patients each were obtained. The negativity rated of the pathological surgical margins were comparable between the two groups before and after propensity score matching. However, the surgical margins were significantly wider in the ICG-FI group before and after propensity score matching (P = .039 and P = .047, respectively).
Conclusion: The ICG-fluorescence imaging technique may offer clinical benefits in terms of a secure surgical margin in laparoscopic partial liver resection.