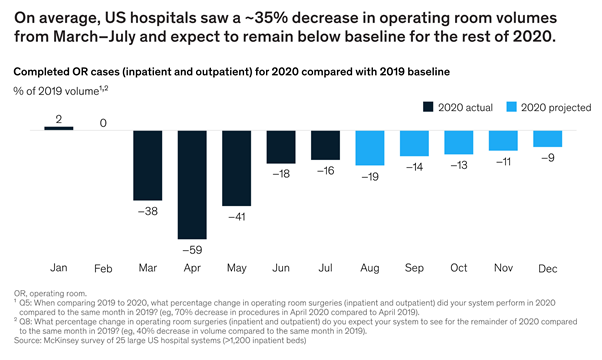
This study investigated whether common elective surgeries have returned to expected levels. The analysis shows that the volume of elective surgeries dropped steeply at the beginning of the pandemic and then increased dramatically when states began reopening and hospitals started offering elective services again for all categories.
No surgical procedure appear to have fully made up the deficit of missed surgeries from early in the pandemic. Knee prosthesis and thyroid or parathyroid surgeries showed the lowest volumes compared to expected in the post-lockdown period, in addition to some of the largest drops in volume during the lockdown period (as defined as July 2021).
https://ehrn.org/articles/elective-surgeries-approach-pre-pandemic-volumes