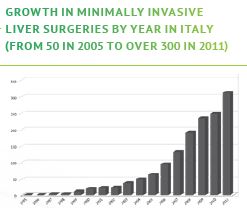
LAPAROSCOPIC LIVER RESECTION (LLR)
Since the first Laparoscopic Liver Resection (LLR) was first preformed in 1991, the number of LLR’s
has increased with the advancements of surgical techniques and technology. LLR for Hepatocellular
Carcinoma (HCC) is now considered standard treatment for minor liver resection.6 Laparoscopic
surgery and robotic surgery have solved the issue of large incisional wounds, a major drawback
of open liver surgery.7 While there are significant advantages associated with a laparoscopic
technique (less bleeding, shorter length of hospital stay, decreased morbidity and possibly lower
mortality), adoption by a surgeon does mean that the ability to touch and palpate the organ is
eliminated. By using ICG in these circumstances, increasing the visualisation of the anatomy adds
enormously to procedure success.